How to operate a drone? It’s a question many ask, intrigued by the possibilities of aerial photography and exploration. This guide provides a structured approach to learning, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and safety regulations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies safely and effectively.
We will explore the intricacies of drone components, providing a clear understanding of their functions and interactions. Mastering the art of takeoff and landing, navigating diverse environments, and understanding essential flight controls are all crucial elements we will cover in detail. Finally, we’ll delve into advanced techniques, safety protocols, and maintenance procedures to ensure you can operate your drone responsibly and efficiently.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section provides a breakdown of key drone parts and introduces essential terminology for beginners.
Drone Component Functions
A drone comprises several key components working in concert. These include:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to lift off and maneuver in the air. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors drive the propellers. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity. Motor size and power directly impact the drone’s flight performance.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this onboard computer processes sensor data (from gyroscopes, accelerometers, and GPS) and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute commands from the remote controller.
- Battery: Provides the power for the motors and other electronic components. Battery capacity (measured in mAh) determines flight time. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are widely used for their high energy density.
- GPS Module (optional): Allows for precise positioning and autonomous flight features such as waypoint navigation and return-to-home functionality.
- Gimbal (optional): A stabilized mounting platform for the camera, ensuring smooth footage even during aggressive maneuvers.
- Camera (optional): Captures photos and videos. Camera quality varies greatly depending on the drone model.
- Remote Controller: Used to control the drone’s movements and camera settings.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms is essential for understanding manuals and online resources.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each motor.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): A sensor system that measures the drone’s orientation and movement.
- mAh (milliampere-hour): A unit of battery capacity.
- Payload: The maximum weight a drone can carry (including camera and other accessories).
- RTF (Ready-To-Fly): A drone that comes fully assembled and ready to fly out of the box.
- FPV (First-Person View): A system that allows the pilot to see what the drone’s camera sees in real-time.
Drone Motor Types
Different drone motors offer distinct performance characteristics.
| Motor Type | Characteristics | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brushed | Simpler design, lower cost | Affordable | Less efficient, shorter lifespan, higher maintenance |
| Brushless | More efficient, longer lifespan, higher power output | Efficient, durable, powerful | Higher cost, more complex |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures

Performing a thorough pre-flight check is paramount for safe drone operation. This ensures all systems are functioning correctly and minimizes the risk of accidents.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously check the following:
- Inspect the drone’s physical condition: Check for any damage to the propellers, arms, or body. Ensure all screws are tight.
- Verify battery level: Ensure the battery is sufficiently charged and not damaged.
- Check the flight controller and GPS signal strength: Confirm that the flight controller is functioning properly and that the GPS signal is strong and stable (if applicable).
- Examine the propellers: Ensure they are securely attached and undamaged.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (if necessary): Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibrating these sensors.
- Check the weather conditions: Avoid flying in high winds, rain, or snow.
- Review the flight area: Ensure you have permission to fly in the chosen location and are aware of any airspace restrictions.
- Confirm remote controller connection: Verify that the remote controller is properly paired with the drone and that the connection is stable.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight procedure would show a sequential flow, starting with visual inspection, then battery check, signal check, and concluding with a final systems check before proceeding to takeoff.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents. Techniques vary depending on environmental conditions.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to get you started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From pre-flight checks to mastering maneuvers, this guide provides a solid foundation for responsible drone operation.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
A smooth takeoff involves gently increasing throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Landing involves a gradual descent, maintaining control and minimizing impact. In windy conditions, a slight tilt into the wind might be necessary for stability during takeoff and landing. Confined spaces require precise control and careful assessment of surrounding obstacles. Different takeoff and landing methods include vertical ascent/descent, angled ascent/descent (useful in confined spaces), and potentially pre-programmed autonomous landing sequences.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers: How To Operate A Drone
Mastering basic flight controls is essential for safe and efficient drone operation. This involves understanding how to control altitude, direction, and speed.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the complexities of flight requires practice and understanding of regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, from basic principles to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will help ensure safe and responsible drone operation.
Basic Flight Control
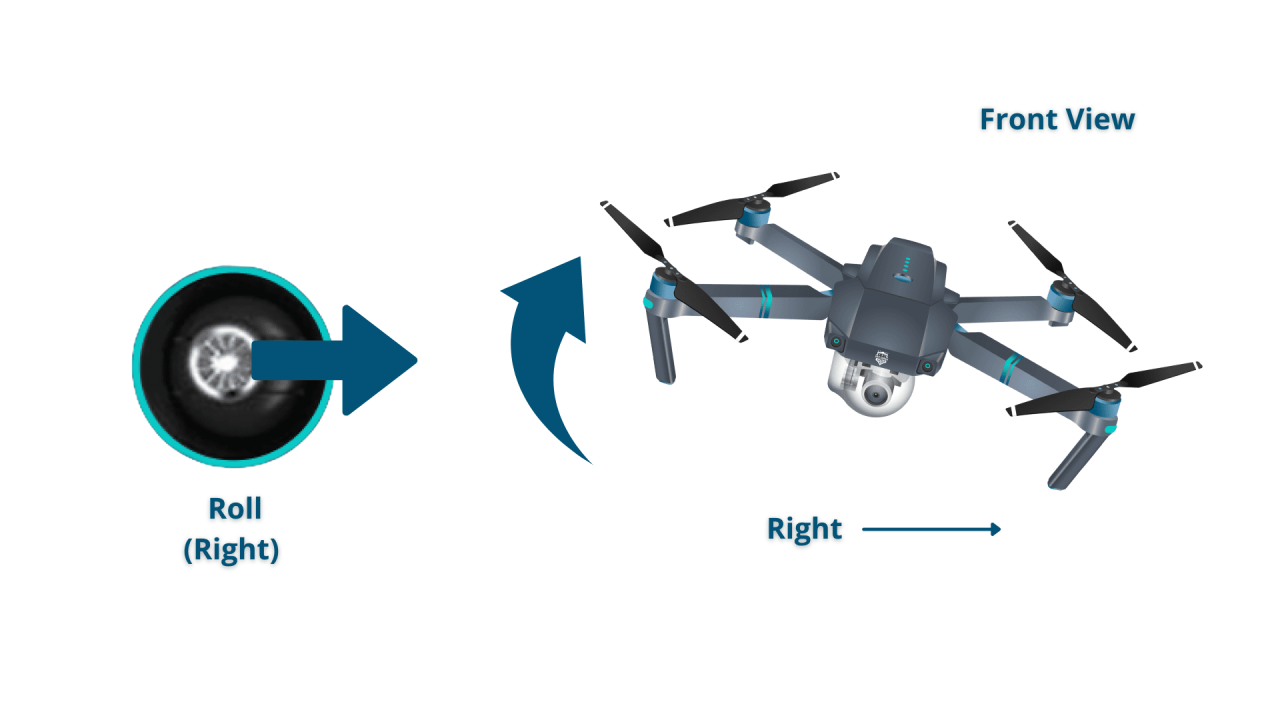
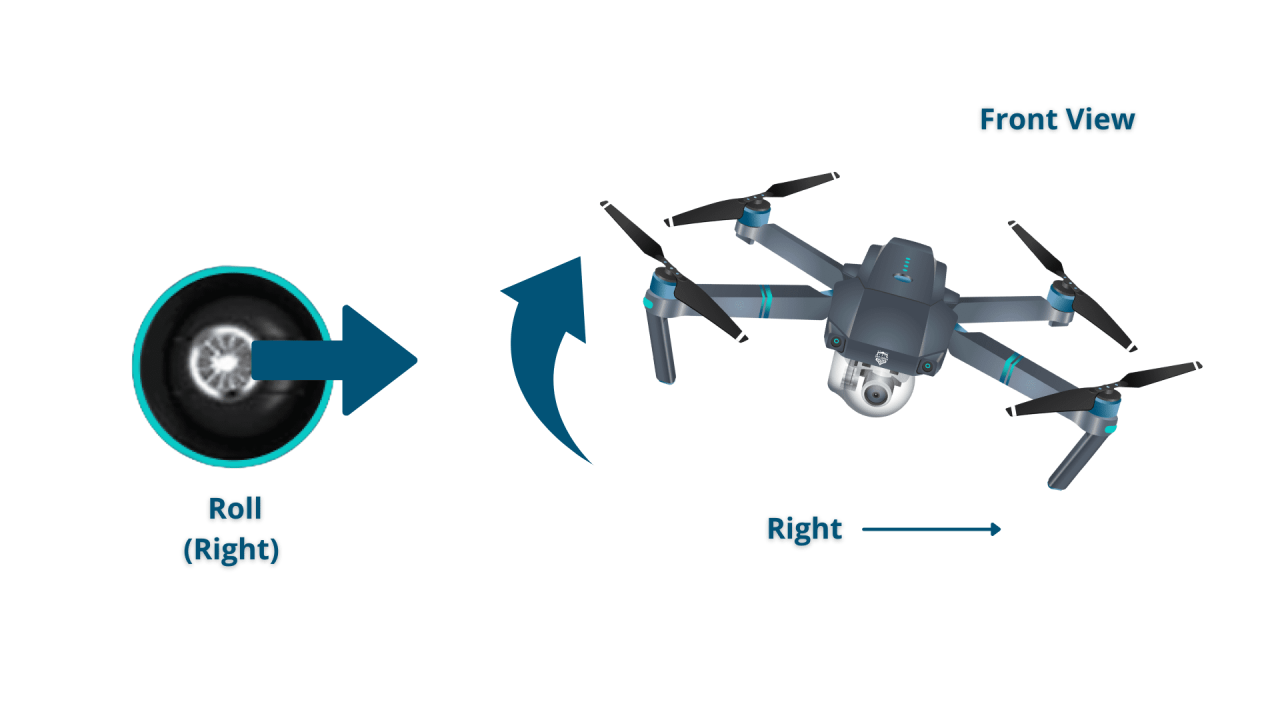
Most drone controllers use two joysticks. One controls the drone’s pitch and roll (forward/backward, left/right movement), while the other controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude). Smooth, precise movements are key. Hovering requires balancing the throttle to maintain a consistent altitude. Turning involves using the yaw control to rotate the drone, while moving sideways involves a combination of pitch/roll and yaw.
Common Flight Control Mistakes
- Sudden movements: Avoid abrupt joystick movements, which can destabilize the drone.
- Ignoring wind conditions: Failure to compensate for wind can lead to loss of control.
- Overestimating battery life: Always have sufficient battery reserve for a safe return.
- Neglecting pre-flight checks: This can result in malfunctions during flight.
Navigating and Orientation
Maintaining visual contact and understanding the drone’s orientation are crucial for safe navigation.
Maintaining Visual Contact
Always keep the drone within your line of sight. If flying beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) is necessary, ensure you comply with all relevant regulations and use appropriate technology.
Navigation Challenges and Solutions
Challenges include wind gusts, GPS signal loss, and obstacles. Solutions involve adjusting flight parameters, selecting appropriate flight modes, and carefully planning the flight path.
Drone Orientation and Controller Stick Movements
A detailed description of this would show a visual mapping of joystick movements to drone orientation. For example, pushing the left stick forward corresponds to the drone moving forward, pushing it right causes the drone to move right, and so on. Yaw control is typically handled by rotating the right joystick.
Advanced Flight Techniques

Advanced techniques enhance flight capabilities and offer greater control.
Advanced Maneuvers and Flight Modes
Waypoint navigation allows pre-programming a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously. Autonomous flight modes, such as follow-me or orbit, provide automated flight capabilities. Different drone models offer varying levels of sophistication in these modes.
Improving Flight Stability and Precision
Tips include practicing smooth control inputs, understanding wind effects, and adjusting flight parameters based on conditions.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Adhering to safety guidelines and regulations is essential for responsible drone operation.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Familiarize yourself with local laws and regulations regarding drone operation. These may include restrictions on flight altitudes, locations, and required certifications.
Safety Considerations
Safe practices include checking weather conditions, maintaining safe distances from people and objects, and properly handling and storing batteries.
Emergency Procedures
- Loss of control: Attempt to regain control using the emergency stop function or by manually bringing the drone down.
- Battery failure: Initiate an immediate descent and landing.
- Malfunction: Attempt to land the drone safely, following manufacturer’s recommendations.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are vital for extending drone lifespan and preventing malfunctions.
Routine Drone Maintenance
A schedule might include weekly visual inspections, monthly cleaning, and periodic recalibration of sensors.
Troubleshooting Guide
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, power switch issue | Charge battery, replace battery, check power switch |
| Drone is unstable in flight | Wind, GPS signal loss, calibration issues | Fly in calmer conditions, check GPS signal, recalibrate sensors |
| Camera malfunction | Software glitch, camera settings, hardware failure | Restart drone, adjust camera settings, seek repair |
Photography and Videography with Drones
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photos and videos.
Camera Settings and Techniques, How to operate a drone
Adjusting settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture are crucial for optimal image quality. Techniques include using different flight paths and angles to create dynamic shots.
Composing Aerial Shots
Effective composition involves using the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other photographic principles to create visually appealing images.
Operating a drone successfully involves a blend of technical understanding and practical application. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, from thorough pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques, you’ll be well-prepared to navigate the world of drone piloting with confidence and skill. Remember, safety and adherence to regulations are paramount. With practice and a commitment to safe operation, the skies are truly your limit.
Expert Answers
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, weather conditions, and flight style. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes of flight time per battery, on average.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a “return-to-home” function that will automatically bring the drone back to its starting point if the signal is lost. Always keep the drone within visual range.
Do I need a license to fly a drone?
Regulations vary by country and region. Check your local laws and regulations before flying. In many places, registration may be required.
How do I clean my drone?
Use a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe down the drone body and propellers. Avoid using harsh chemicals or water.